
There is a common misconception that Bitcoin is completely anonymous, it is not. Even though Bitcoin transactions do not involve the transmission of personal details like banking transactions, they are not entirely anonymous.
Bitcoin users can protect their identity to some extent, but their transactions can be tracked to the address where they receive the bitcoins. If the user links the address to their personal identity, all the associated transactions will be linked to that identity.
What Is Blockchain and How Bitcoin Works?
The blockchain is a publicly shared digital ledger in which each transaction is unchangeable, time-stamped and linked to the previous one. The blockchain updates only through the consensus of participants and data that enters the blockchain can never be erased.
A blockchain is a peer-to-peer network that does not need an administrator to complete the transactions between different parties. Each transaction or digital record is called a block and it is linked to a specific address.
Each block that stores a specific transaction goes into the blockchain as a permanent entry in the publicly available database. Blocks are connected to each other in a linear fashion to make a chain and each block stores the hash of the previous block.
The blockchain transactions are immutable and they cannot be deleted. Cryptography is used to add the blocks to the chain to make sure that nobody meddles with the blockchain.
How Secure Is Blockchain?
To complete any transaction and move anything of value from the blockchain, the network must validate the transaction. To hack a blockchain, you won’t just need to hack one system, but each system on the network.
Advantages of Blockchain
- The cost of storing the electronic ledgers in the form of a Blockchain is much cheaper than the traditional accounting systems.
- The Distributed Ledger Technology(DLT) such as a blockchain results in fewer errors and makes the process faster.
- Less capital is required to be held against the risks of transactions that are pending.
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency based on the blockchain technology. It is a form of digital currency held electronically by the users and they are decentralized, i.e., no single institution controls them.
Instead of being printed physically by an institution, they come into existence when they are mined. Bitcoins are mined electronically using the computing power in a distributed network.
Bitcoin Mining
Mining secures the Bitcoin network and processes every Bitcoin transaction. Bitcoin miners solve complex computational problems that allow them to chain together the blocks or transactions.
Miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoins and transaction fees. According to the current rules, there will be 21 million bitcoins ever mined.
Bitcoin Transactions
A user needs a Bitcoin Wallet to complete a Bitcoin transaction. Using a Bitcoin wallet, you can generate a Bitcoin address.
A Bitcoin wallet is an app or a program that can be installed on a computer, a smartphone or accessed using a web browser. It can be used to generate new Bitcoin addresses, store Bitcoins, send Bitcoins and receive Bitcoins.
Every Bitcoin wallet has a private key which acts as a password for the wallet. The private key is used to generate a Bitcoin address.
A Bitcoin wallet can be compared to an email client such as Outlook and Bitcoin address can be compared to an email address. Just like emails are sent and received using different email addresses, Bitcoins are sent and received using different Bitcoin addresses.
A Bitcoin transaction is a transfer of value from one Bitcoin address to another Bitcoin address using the private key and the Bitcoin Wallet. The Bitcoin wallet interacts with the Blockchain and updates the entries on the network and the user interface.
When a user sends Bitcoins to another user, the transaction needs to be confirmed by the Bitcoin network. Large transactions typically need multiple confirmations for enhanced security.
Balances
All confirmed transactions are included on the blockchain network. Bitcoin wallets can interact with the Bitcoin network and calculate the spendable balance in the user’s account.
Tracing Bitcoin Owners
Bitcoin network needs Bitcoin addresses to allocate Bitcoins. Your identity is not recorded on the Bitcoin Blockchain network, but the Bitcoin address you use is stored on the network.
As all the transactions are publicly broadcast, everybody is able to see the flow of Bitcoins across different addresses. However, no personal information of the person holding the Bitcoin address is stored over the Blockchain network.
Many users access Bitcoin services using various services that need disclosure of their personal information. The service providers can trace the users behind the Bitcoin addresses and also disclose that information to third-parties such as law enforcement agencies.
Compromising Bitcoin Anonymity
– Connecting Nodes
It is possible for the hackers to connect multiple nodes to find the origin of a transaction.
– Transaction Ledger
As Bitcoin transactions are publicly shared, Bitcoin addresses can be traced. You can tie a group of different addresses to a particular user
– Transaction Graph Analysis
It exploits a Bitcoin feature called ‘Change’, besides employing many other techniques. Whenever the output of a Bitcoin transaction is used as the input of another transaction, the amount must be spent in its entirety.
Bitcoin transactions don’t allow the partial spending of the total number of bitcoins held by a given address. To send a partial amount to another user, the user has to spend the remaining amount to his own address.
The amount sent back by the user to his own address is sent to the wallet’s change address. This information can be combined with other techniques to reveal more information about the user and track his identity.
Best Methods To Enhance Your Privacy as much as possible Using Bitcoin
– Using HD Wallets (Hierarchical Deterministic)
HD Wallets like the Ledger Nano S, MyCelium or the Trezor will create a new addresses each time you use them.
Consider a wallet which acts like your keychain, and then each address as a different key on that chain.
Reusing the same keys will give you away. The HD wallet scrambles up your keys each time you use them.
Multiple addresses will help you enhance your privacy over the Bitcoin network.
– Mixing Services

Mixing services blend different user’s Bitcoins together and make it impossible to track the connections. Mixing services can truly enhance your privacy, but you need to trust the mixing services with your Bitcoins.
This process essentially breaks the link-ability by creating temporary addresses or by switching your coins with other addresses with similar amounts. This essentially erases your trace-ability.
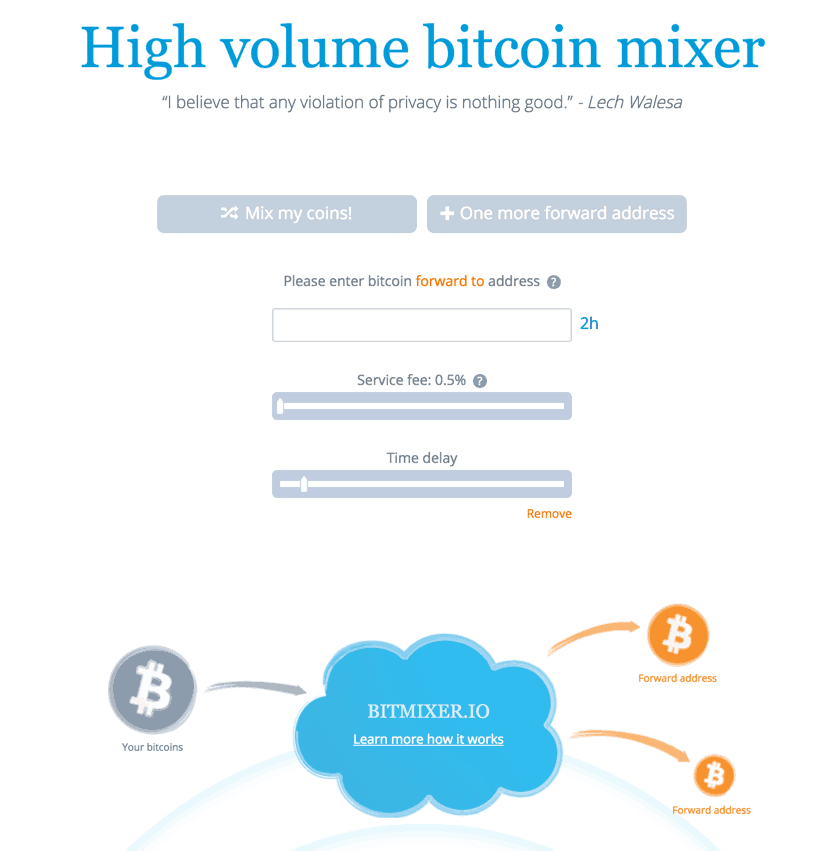
This mixing site bitmixer was one of these Bitcoin mixers, but has since shut down. The other service you could try is Helix.
– Using LocalBitcoins.com to transact. Exchanges would normally require you to verify your identity with their KYC rule, you can access Localbitcoins using a VPN or Tor and create an account with a pseudonym and a burner email/phone number.

To Sum Up
Bitcoin network is not as private or anonymous as it is believed to be. As all the transactions are recorded on a publicly distributed ledger, it boosts transparency but makes Bitcoin less anonymous than cash.




Browser Tor + bitcoin wallet (link omitted) = 100% anonymity.